Sparta, Greece
”Conscious of the past, efforts were made at the time to rebuild the town so as to reflect its ancient pre-eminence, but the town planners fell someway short. In their defence, they did not have a lot to work with; it’s obvious Ancient Sparta was more focused on building legendary armies as opposed to cities. Also, it’s hard for a structure to outlive antiquity if it was never constructed in the first place.”
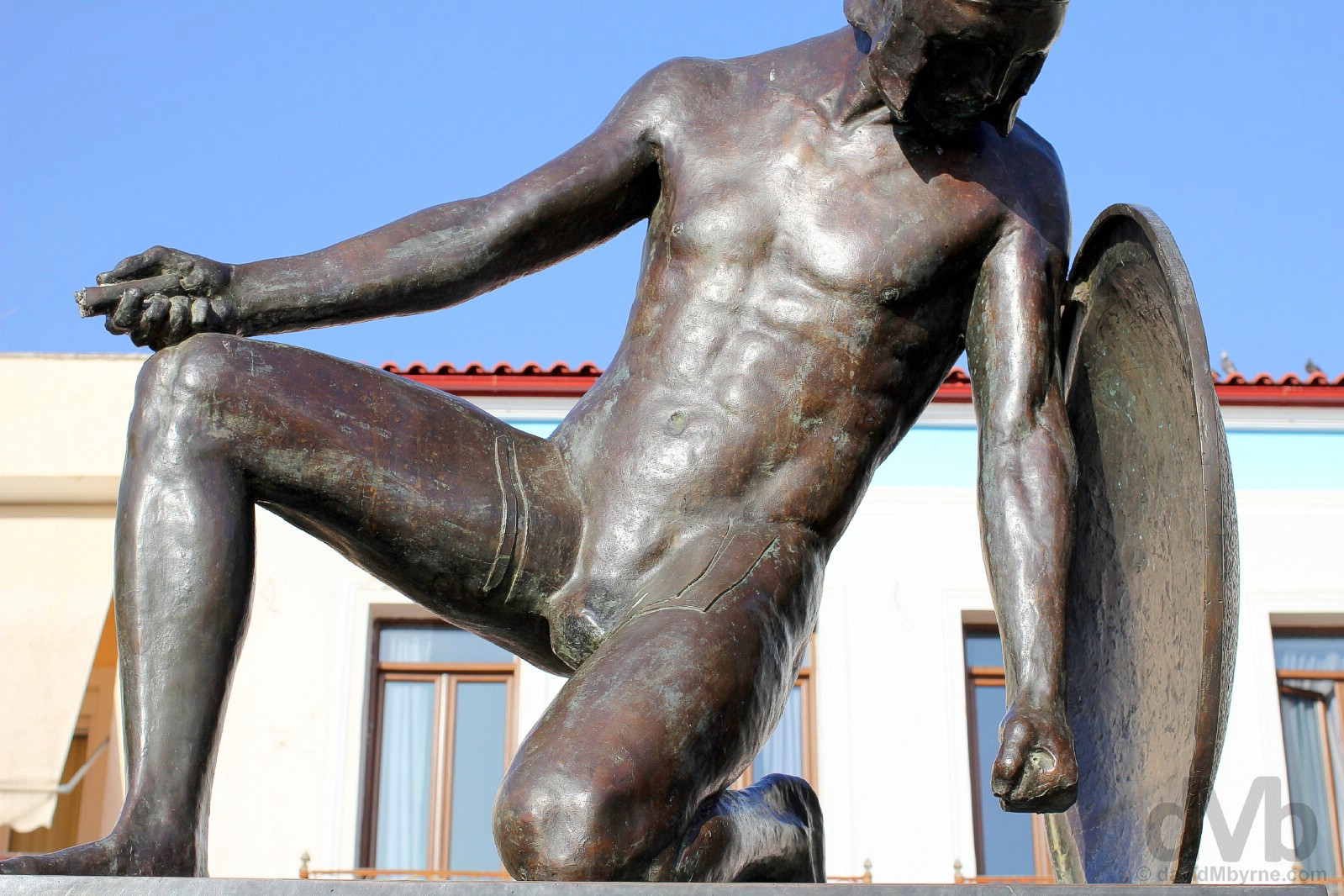
Image || The King Leonidas Statue, Sparta, Peloponnese, Greece. May 7, 2017.
Sparta, Peloponnese, Greece
It is safe to say that the legend of Ancient Sparta, Greece’s once-dominant and inviolable city-state and military land-power, is more of a draw than the agreeable but unassuming present-day Greek settlement.
This is Sparta. Sparta, Peloponnese, Greece. May 7, 2017.
dMb Country Overview - Greece
 Greece
Greece
Region – Southeastern Europe/The Balkans (dMb tag: The Balkans). Capital – Athens. Population – 10.8 million. Official Language – Greek. Currency – Euro (€) GDP (nominal) per capita – US$21,000 Political System – Unitary parliamentary republic. EU Member? – Yes (10th member joined January 1981). UN Member? – Yes (founding member joined October 1945). G20 Member? – No. Size – 132,000 km² (Europe’s 15th largest country is approximately half the size of Ecuador, twice the size of Sri Lanka, and roughly the same size as the US southern states of Alabama and Louisiana. Topography – A mountainous interior (80% of Greece is mountainous), a long and convoluted coastline, and hundreds of offshore islands. Independence – 1830 from the Ottoman Empire following 1821 to 1830 Greek War of Independence. Brief History – From the eighth century BC, the Greeks were organised into various independent city-states, known as poleis (singular polis), which spanned the entire Mediterranean region and the Black Sea. Philip of Macedon united most of the Greek mainland in the fourth century BC, with his son Alexander the Great rapidly conquering much of the ancient world, from the eastern Mediterranean to India. Greece was annexed by Rome in the second century BC, becoming an integral part of the Roman Empire and its successor, the Byzantine Empire, which adopted the Greek language and culture. The Greek Orthodox Church, which emerged in the first century AD, helped shape modern Greek identity and transmitted Greek traditions to the wider Orthodox World. After falling under Ottoman dominion in the mid-15th century, Greece emerged as a modern nation state in 1830 following a war of independence. UNESCO World Heritage sites – 18. Tourism Catchphrase/Slogan – All Time Classic. Famous For – Endless coastline and beaches; shipping; democracy (born here); a classical and hallowed past; ouzo; sun-drenched islands; Alexander the Great; the Olympics; being the cradle of Western civilisation; food (tzatziki, feta, souvlaki, moussakas, yogurt, grapes, olives and olive oil); economic collapse & austerity.
Ouzo for sale in the village of Oia, Santoríni, Cyclades, Greece.

Ouzo for sale in the village of Oia, Santoríni, Cyclades, Greece.
Highlights – Cyclades island-hopping and the remnants of all that ancient history (Greece boasts four millennia of sun-bleached ruins, artefacts, and architecture). Greece Titbits – At nearly 14,000 km (8,500 miles), Greece has the 11th longest coastline in the world; Greece is considered the cradle of Western civilisation, being the birthplace of democracy, Western philosophy, Western literature, historiography, political science, major scientific and mathematical principles, Western drama, and the Olympic Games (the country’s rich historical legacy is reflected in part by its 18 UNESCO World Heritage Sites, as of 2017); the Greek economy is the largest in the region with an economy larger than all other Balkan countries combined, this despite its well-documented economic battering and subsequent austerity measures.
Visits – 2 (May 2008 and April/May 2017). Where I Went/What I Saw – Thessaloniki; The Cyclades (Santoríni, Paros, Mykonos, Delos, Tinos); Zakynthos/Zante; Olympia; Sparta; Mystras; Athens.
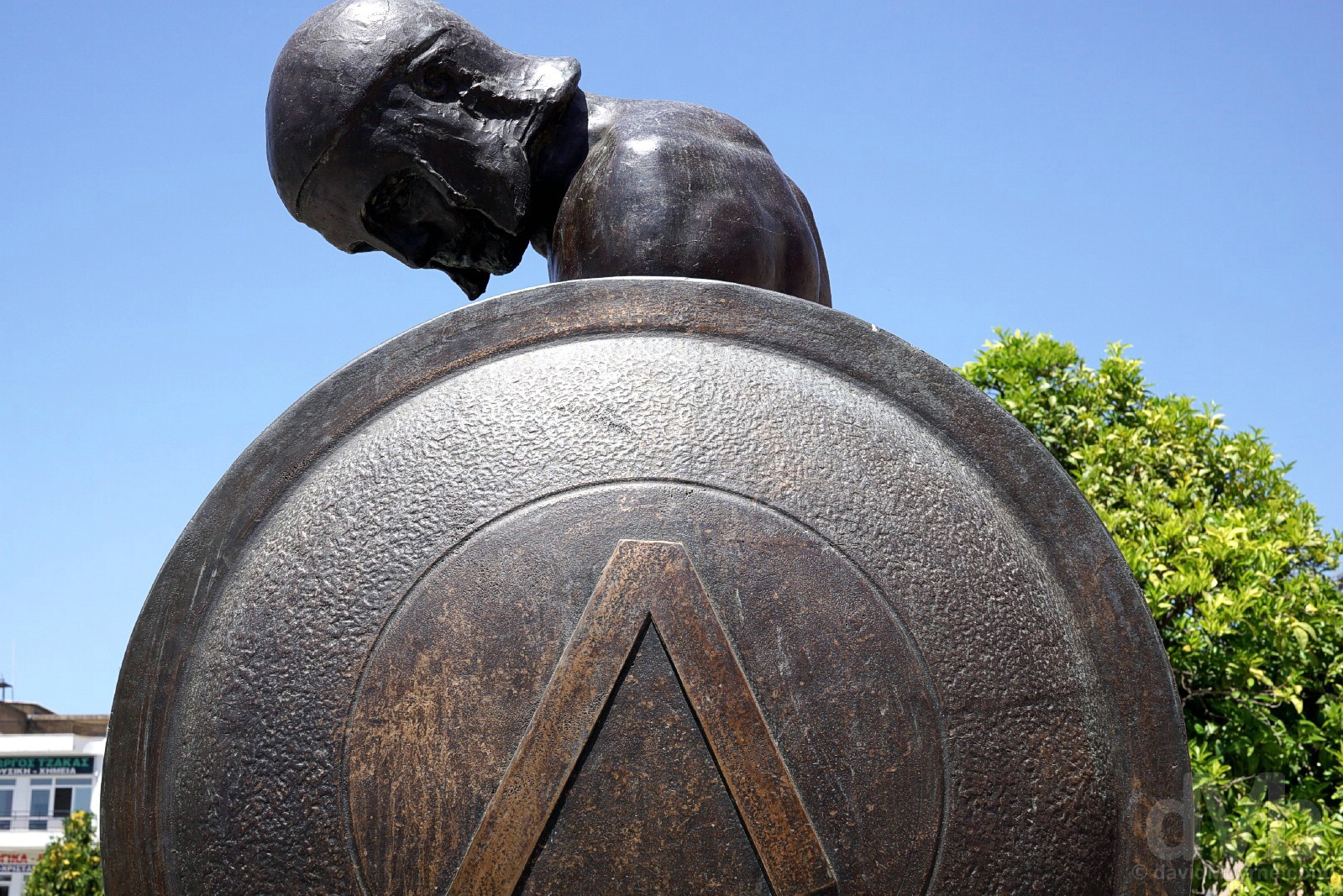
LAMBDA / LACEDAEMON | A Spartan soldier with his shield on display in present-day Sparta’s central plaza, Plateia Kentriki. The shield bears the letter lambda, the 11th letter of the Greek alphabet, the symbol the Spartan army used to denote Lacedaemon, as the feared city-state was known in antiquity. Sparta, Peloponnese, Greece. May 8, 2017.
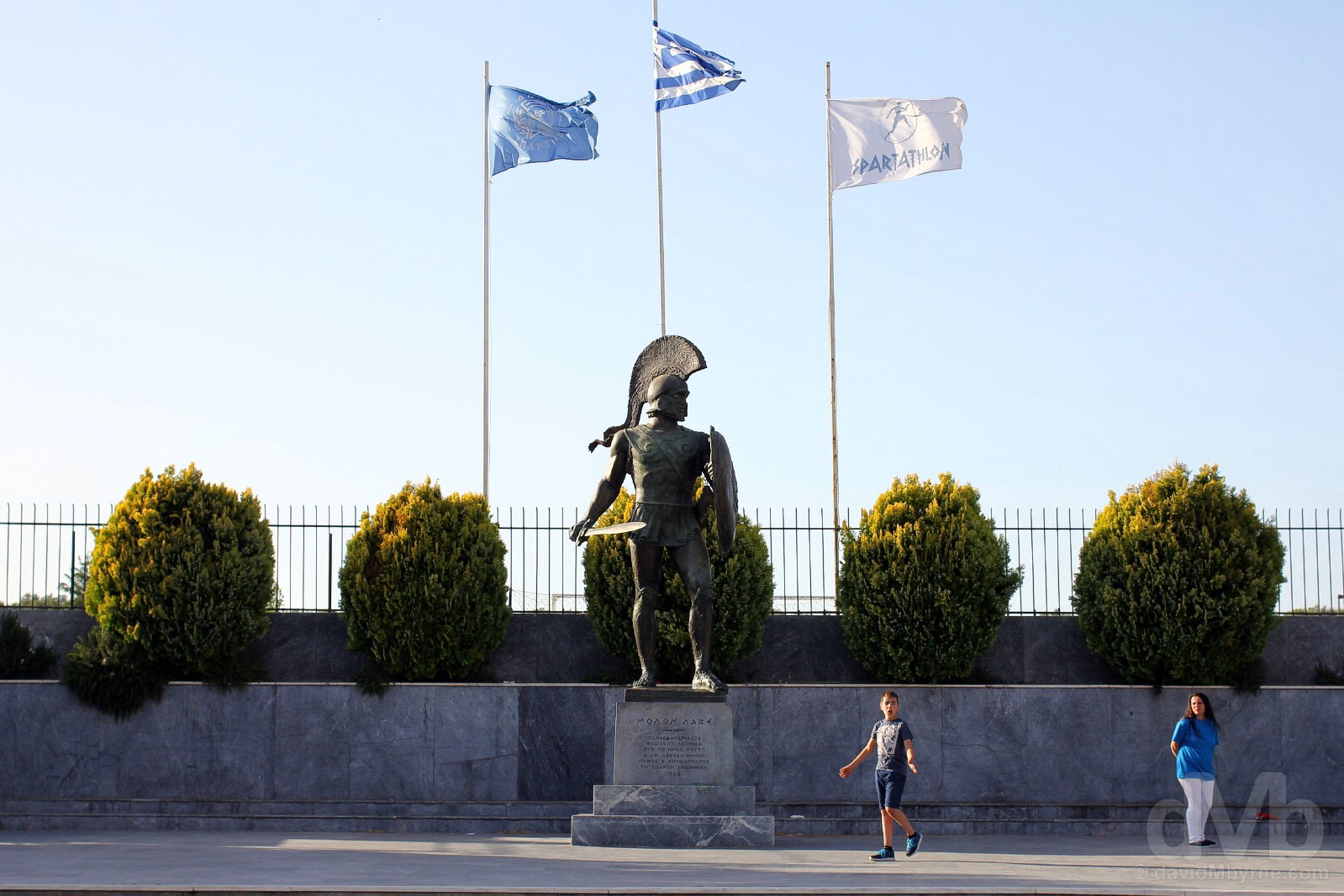

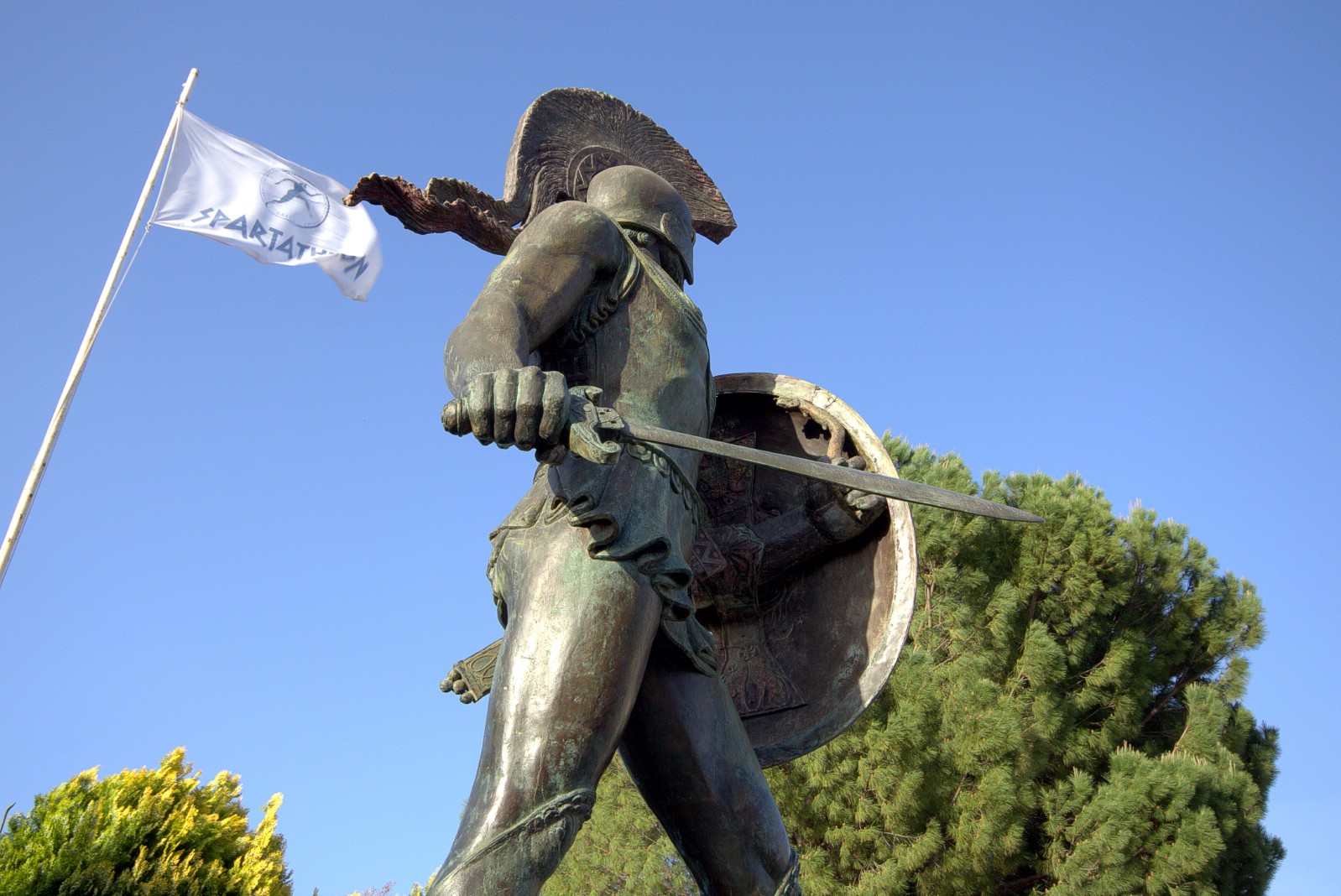
KING LEONIDAS STATUE |The King Leonidas Statue, Sparta, Peloponnese, Greece. May 7, 2017.
The warrior King Leonidas I (c. 540 – 480 BC) attained martyrdom by leading an coalition of Greek forces, including some 300 Spartans, to a last stand against a vastly superior numerical force of Persians at the Battle of Thermopylae, an event recounted in the 1962 epic The 300 Spartans, 2007s 300 and 2014s 300: Rise of an Empire. Despite the odds the Spartans, and not surprisingly, refused to flee or surrender. Sparta’s King Leonidas Statue, portraying a defiant and proud king, was erected in 1968 and bears the inscription ‘Molon labe’ (‘Come and get them’), seemingly the king’s response to the attacking Persian army’s demand for the outnumbered Spartans to lay down their weapons and surrender.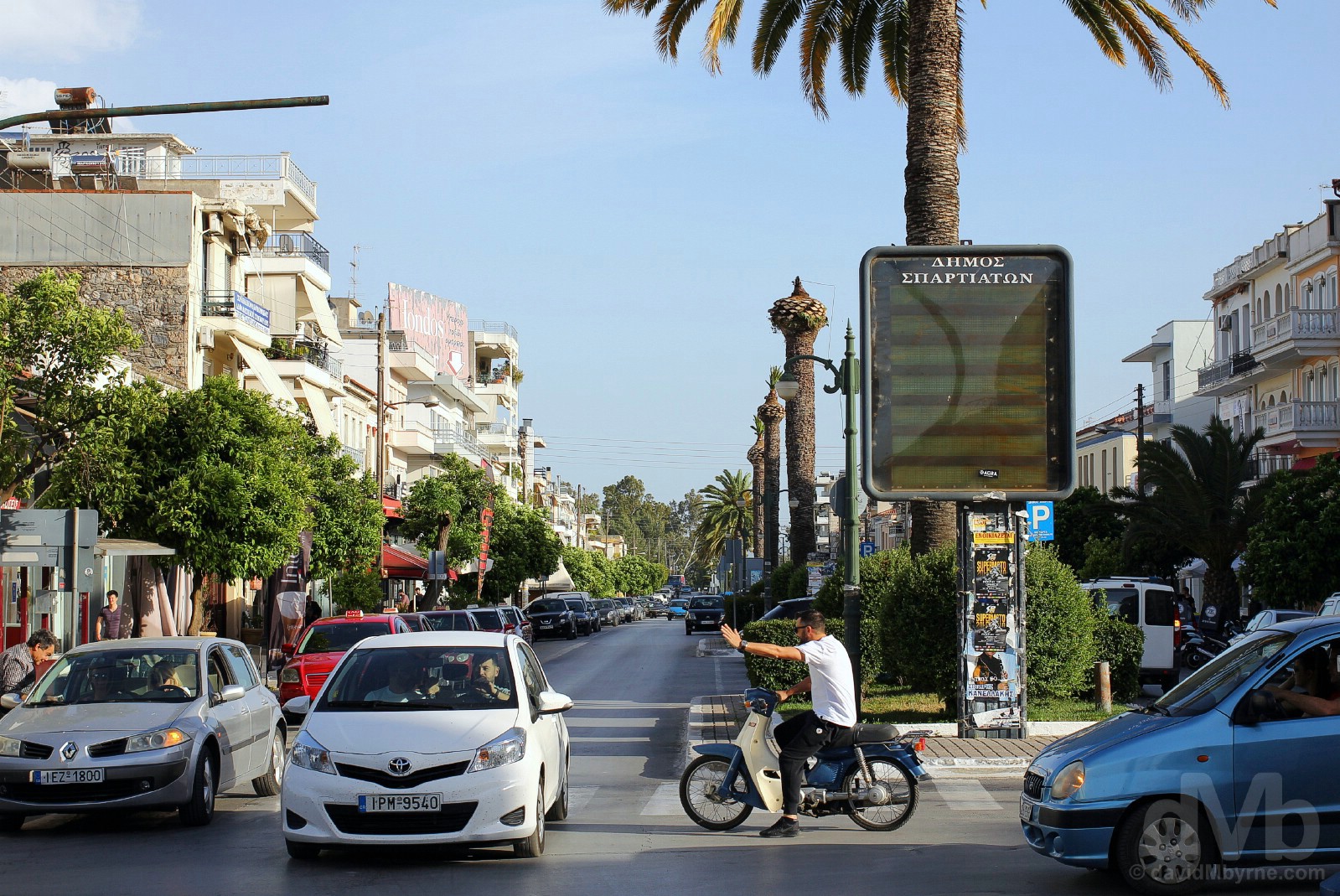
MODERN SPARTA |Traffic mayhem approaching sunset on tree-lined Leof. Likourgou, Sparta, Peloponnese, Greece. May 7, 2017.
– Thucydides, Athenian historian and general, c. 460-400 BC
The 1880s design of modern-day Sparta was headed by Bavarian city planners who ensured the town would have large squares and wide tree-lined streets. Conscious of the past, efforts were made at the time to rebuild the town so as to reflect its ancient pre-eminence, but the town planners fell someway short. In their defence, they did not have a lot to work with; it’s obvious Ancient Sparta was more focused on building legendary armies as opposed to cities. Plus, it’s hard for a structure to outlive antiquity if it was never constructed in the first place.– Lykurgos, architect of the warlike Spartan constitution and society, c. 820 BC
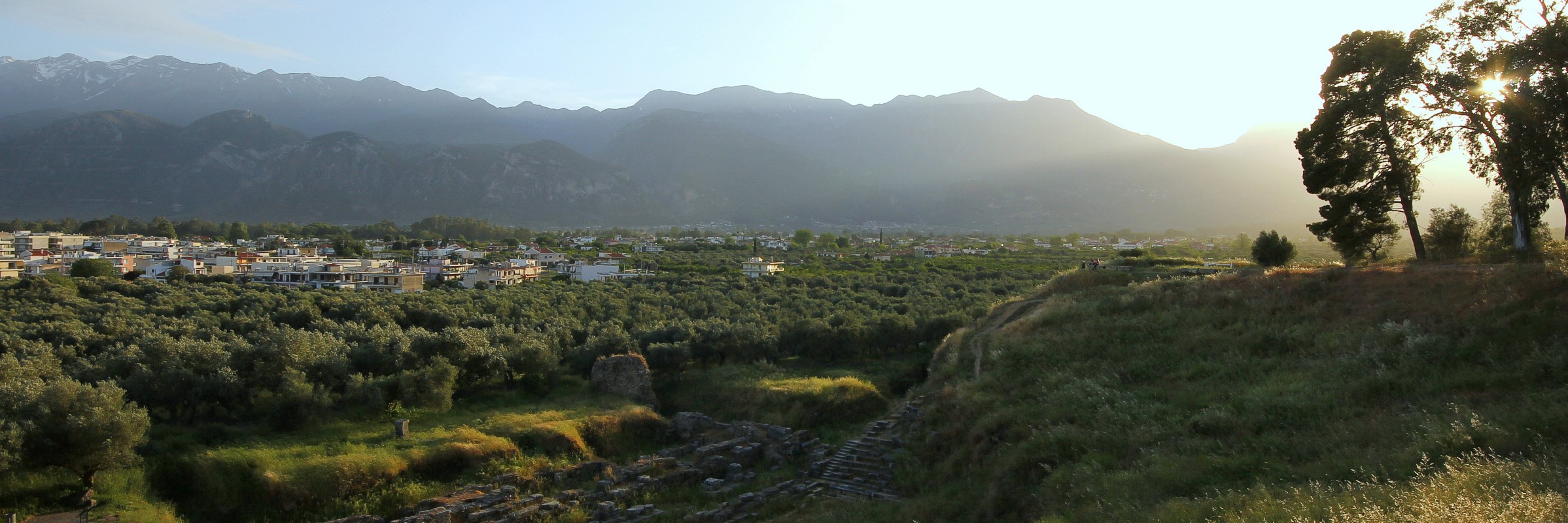

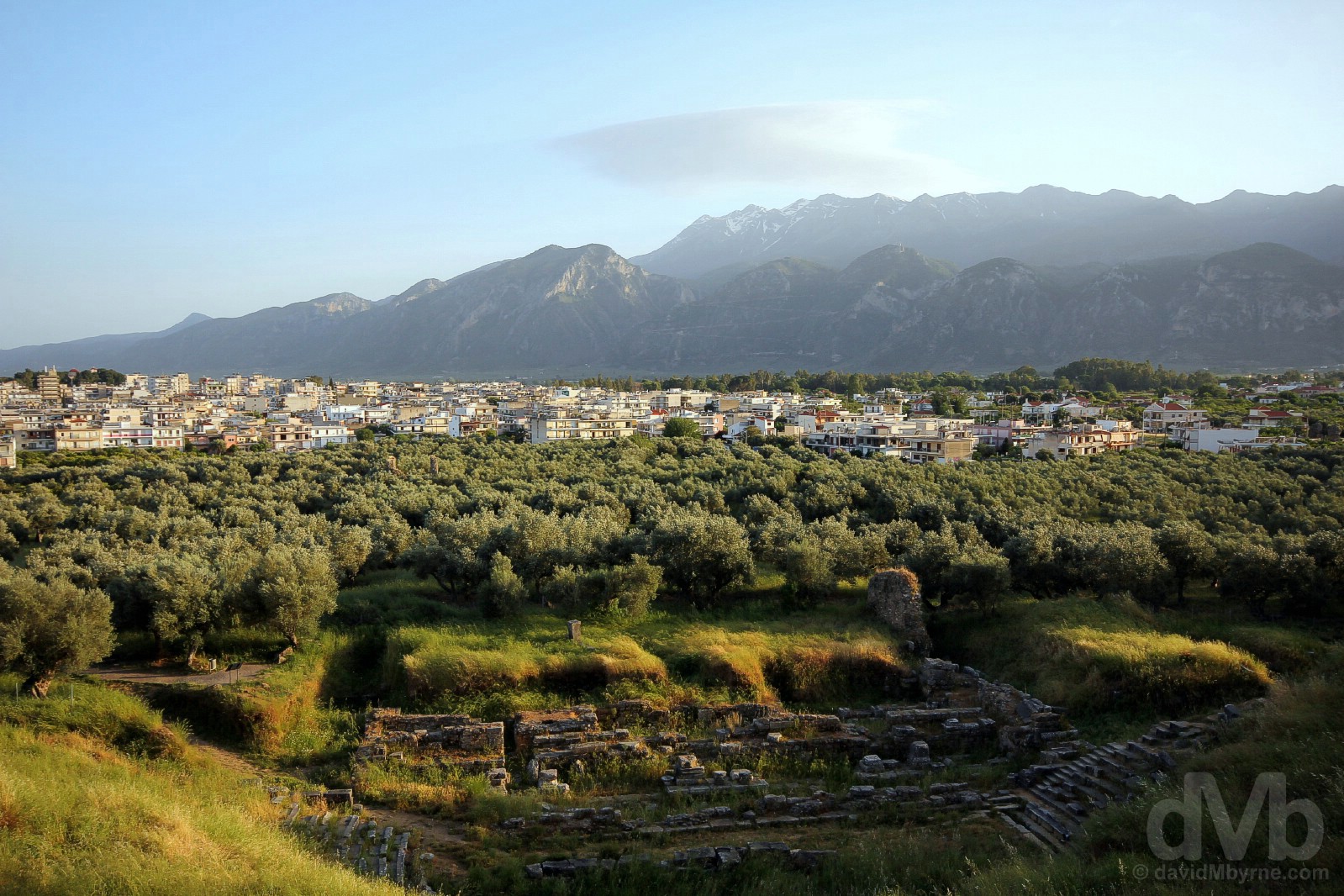
OLD ACROPOLIS THEATRE | Approching sunset at the ruins of the Theatre of the Old Acropolis of Ancient Sparta with the buildings of modern-day Sparta in the Evrotas River Valley overlooked by the Taygetus mountain ridge, Peloponnese, Greece. May 7, 2017.
Sadly, very little of Ancient Sparta survives to this day, although remnants of the once-great city-state do remain. Set among the grassy hillside to the north of present-day Sparta is the site of the Old Acropolis and Agora of Ancient Sparta, or what’s left of it (not a lot), the religious and administrative centre of the settlement from the 8th century BC until the Roman era. The remains of the 1st century BC semi-circular Ancient Theatre are probably Ancient Sparta’s most famous ruin, surviving today as nothing more than a partial retaining wall and a few seats and steps, all of which seems to be fighting a losing battle against encroachment by the unchecked surrounding greenery. It was all a bit of a let-down, especially having arrived here from the fascinating archaeological ruins of Ancient Olympia, except, of course, for the sunset vista of present-day Sparta sitting in the Evrotas River Valley and lorded over by the massive wall of the Taygetus mountain ridge – the sunset views over the valley from the tallest of the Spartan hills was awesome.

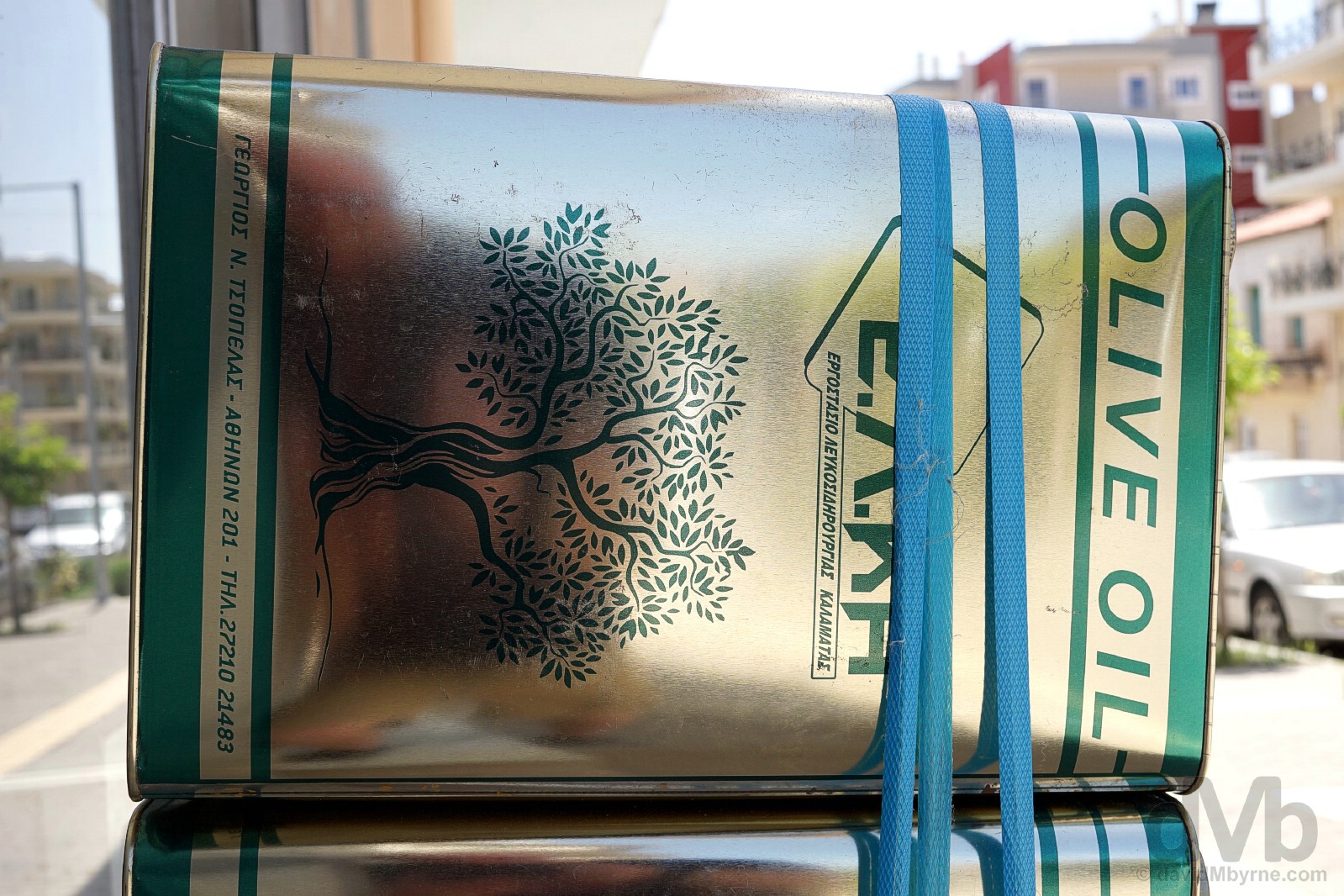
OLIVE MUSEUM | A display in the Museum of the Olive & Greek Olive Oil, Sparta, Peloponnese, Greece. May 8, 2017.
As a regional centre for the processing of olives (and citrus fruit), I wasn’t surprised to learn that Sparta had a museum dedicated to the small ovoid fruit of the European olive tree, especially as Greece is the third highest producer of olives on earth and that the Greeks themselves are the highest per capita consumers of olive oil. I was surprised, however, that I paid it a visit – I’m not a fan (of olives) – but I’ll freely admit to enjoying my visit to the immaculately presented museum, which delves into all things olive and olive oil, from its initial appearance in the Mediterranean in c. 8,000 BC to the many practical usages for its oil (cooking, fuel, ritual, perfume-making). The beautifully designed exhibition spaces cover a few airy floors and even spill outdoors to the courtyard where one will find reconstructions of olive presses and pressing technology dating from prehistoric to Byzantine times. Definitely worth a look.Signing Off | The Complete Sparta Gallery





